
Understanding the Purpose of a CT Scan
A CT scan provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body, helping diagnose conditions, monitor treatment progress, and guide medical procedures․ It’s essential for detecting internal injuries, tumors, and structural abnormalities․
Diagnostic Uses of CT Scans
CT scans are widely used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including injuries, tumors, infections, and vascular diseases․ They are particularly effective in detecting small lung nodules, abdominal abnormalities, and brain injuries․ The detailed images help identify internal structures, guiding precise treatment plans and monitoring disease progression․ CT scans are also essential for evaluating chest pain, shortness of breath, and hematuria, making them a critical tool in emergency and routine diagnostics․
Screening vs․ Diagnostic CT Scans
Screening CT scans are used to detect early signs of disease in asymptomatic individuals, such as lung cancer in high-risk patients․ Diagnostic CT scans, however, are employed to investigate symptoms or abnormalities already identified․ Both utilize detailed imaging but differ in purpose: screening aims at prevention, while diagnostics focus on confirming and managing existing conditions, ensuring appropriate treatment plans are formulated based on accurate findings․
Factors to Consider Before Ordering a CT Scan
Consider radiation exposure risks, patient age, pregnancy status, and allergies to contrast agents․ Evaluate medical necessity and alternative imaging options to ensure informed decision-making․
Radiation Exposure and Safety Concerns
Radiation exposure is a critical consideration when ordering a CT scan․ While CT scans are valuable for diagnosis, they emit higher radiation levels than standard X-rays․ The risks, including potential cancer concerns, must be weighed against the diagnostic benefits․ Modern machines offer low-dose options to minimize exposure․ Special precautions are necessary for children, pregnant women, and those requiring frequent scans․ Providers should ensure scans are medically justified to avoid unnecessary radiation risks․
Contrast Agents and Allergies
Contrast agents are often used in CT scans to enhance image clarity, but they can cause allergic reactions․ Patients must inform their doctors of any allergies or previous adverse reactions․ Common symptoms include hives, itching, or difficulty breathing․ In severe cases, life-threatening anaphylaxis can occur․ Premedication with corticosteroids may be recommended for high-risk individuals․ Additionally, breastfeeding mothers should avoid nursing for 24-48 hours after contrast administration to ensure safety․

Preparing Patients for a CT Scan
Prior to a CT scan, patients should inform their doctor if pregnant or breastfeeding․ They should avoid jewelry, wear loose clothing, follow dietary instructions, and arrive early for preparation․
General Preparation Instructions
Patients should inform their doctor if pregnant or breastfeeding․ They must avoid jewelry, wear loose clothing, and arrive 30 minutes early․
Food intake may be restricted based on the body part being scanned․
Patients should follow specific instructions provided by their healthcare provider for the best imaging results․
Special Considerations for Contrast Dye
Patients must inform their doctor about allergies, especially to iodine or prior contrast reactions․ Women should disclose pregnancy or breastfeeding, as contrast may require switching to formula for 24-48 hours post-scan․
Diabetics or those with kidney issues need pre-clearance․ Medications may require adjustment, and patients should avoid food or drink as directed for optimal imaging results․

Common Indications for CT Scans
CT scans are commonly used to diagnose injuries, cancers, and internal organ issues․ They are often recommended for evaluating the brain, chest, abdomen, and extremities for abnormalities․
Head and Brain CT Scans
A head or brain CT scan is commonly used to diagnose injuries, strokes, tumors, and structural abnormalities․ It provides detailed images of brain tissue, blood vessels, and skull bones; This non-invasive test is crucial for evaluating symptoms like headaches, seizures, or trauma․ It helps guide treatment decisions and monitor progress․ CT scans are fast and effective, making them ideal for emergency situations․ Discussing radiation exposure with your healthcare provider is important, especially for pregnant or breastfeeding patients․
Chest and Abdomen CT Scans
Chest and abdomen CT scans are essential for diagnosing lung nodules, infections, and abdominal organ issues․ They detect injuries, tumors, and vascular diseases․ Contrast agents enhance image clarity, aiding in detailed examinations․ These scans are particularly effective in emergencies, such as detecting internal bleeding or pulmonary embolism․ They also monitor treatment response for cancers and chronic conditions․ Radiation exposure and contrast allergies must be considered, especially for sensitive patients;

Choosing the Right Type of CT Scan
The choice between low-dose and standard CT scans depends on the patient’s condition and radiation sensitivity․ Contrast-enhanced scans provide better detail for certain diagnoses but require allergy considerations․
Low-Dose vs․ Standard CT Scans
Low-dose CT scans reduce radiation exposure while maintaining image quality, making them ideal for screening and sensitive populations․ Standard CT scans offer higher detail, suited for complex diagnostics․ Choosing between them balances diagnostic needs and radiation risks, ensuring optimal patient care and safety․
With or Without Contrast
CT scans can be performed with or without contrast dye․ Contrast enhances image clarity, highlighting specific tissues or organs for better diagnosis․ It’s often used to detect tumors, infections, or vascular issues․ However, it may not be necessary for routine exams․ Patients with allergies or kidney issues may require alternative approaches․ Informing the doctor about medical history and concerns is crucial to determine the appropriate use of contrast․
Documentation and Ordering Guidelines
CT scan orders require specific details, including the body part, reason for the exam, and whether contrast is needed․ Accurate documentation ensures proper procedure selection and compliance with guidelines․
Required Information for CT Orders
CT orders must include the body part to be scanned, the clinical reason for the exam, and whether oral or IV contrast is needed․ Additional details such as patient history, symptoms, and prior imaging results are often required to ensure the scan is tailored to the patient’s needs․ This information helps radiologists determine the appropriate protocol and ensures accurate diagnostic results․ Proper documentation is essential for insurance approval and pre-certification processes․
Insurance and Pre-Certification Requirements
Insurance companies often require pre-certification for CT scans to ensure the procedure is medically necessary․ Providers must submit clinical justification, patient history, and imaging needs․ Documentation should include the reason for the scan, symptoms, and relevant medical history․ Pre-authorization may vary by insurer, and some may require additional information or adherence to specific clinical guidelines․ Patients should verify coverage before the procedure to avoid unexpected costs․

Special Considerations
Special considerations include pregnancy, breastfeeding, and emergency situations․ CT scans during pregnancy are used cautiously, while breastfeeding may require temporary formula use if contrast is administered․ Emergencies often bypass pre-authorization․
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
CT scans during pregnancy are cautiously considered due to radiation exposure risks․ Breastfeeding mothers may need to use formula for 1-2 days after contrast dye administration․ Always inform the doctor of pregnancy or breastfeeding status to ensure safe imaging practices and minimize potential risks to the baby․
Emergency and Urgent CT Scans
CT scans are critical in emergency situations for quickly diagnosing life-threatening conditions like internal bleeding, pulmonary embolism, or stroke․ They provide rapid, detailed imaging essential for guiding immediate treatment․ Urgent CT scans prioritize patients with acute symptoms, ensuring timely intervention․ Hospitals often have 24/7 CT availability to handle emergencies, minimizing delays and maximizing diagnostic accuracy for critical care situations․

Understanding CT Scan Results
CT scan results provide detailed images of internal structures, aiding in diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring progress․ They help identify abnormalities, injuries, or diseases with precision․
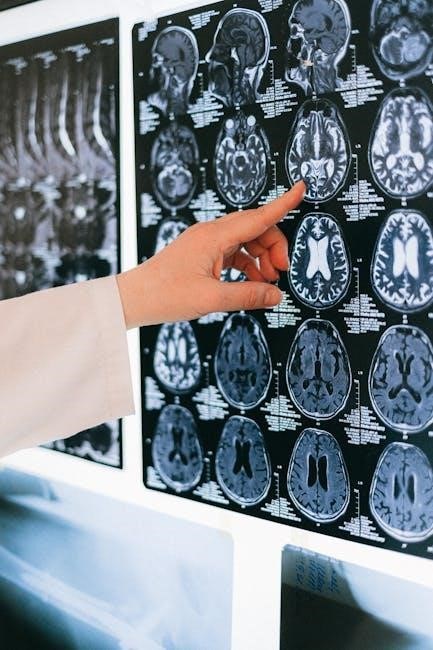
Interpreting CT Scan Images
CT scan images are analyzed by radiologists to identify abnormalities, such as tumors, fractures, or organ damage․ Contrast agents enhance image clarity, aiding in accurate diagnoses․ The interpretation is based on clinical context and expertise․
Follow-Up and Next Steps
After a CT scan, follow-up imaging may be needed to monitor conditions or confirm diagnoses․ Patients should discuss results with their doctor to determine next steps, such as additional tests or specialist referrals․ Clear communication ensures appropriate treatment plans are implemented promptly․
Patient Education and Communication
Ensuring patients understand the CT scan process reduces anxiety and improves cooperation․ Clear communication about expectations and results helps patients make informed decisions about their care․
Explaining the Procedure to Patients
Explain that a CT scan is a non-invasive, painless imaging test using X-rays to create detailed body images․ Emphasize the importance of wearing comfortable clothing, avoiding jewelry, and following preparation instructions․ During the scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large machine, where they must remain still and follow breathing instructions․ Contrast dye may be used to enhance image clarity․ Reassure patients it’s a quick, safe process and address any concerns they may have․
Addressing Patient Concerns and Anxiety
Address patient concerns by explaining the CT scan’s safety and benefits․ Reassure them the procedure is painless and quick, with minimal radiation exposure․ Discuss concerns about contrast dye allergies and pregnancy․ Emphasize the importance of informing the doctor of any medical history․ Explain the non-invasive nature of the scan and the open design of the machine to ease claustrophobia fears․ Encourage questions to reduce anxiety and ensure they feel informed and comfortable․